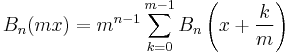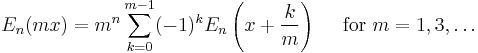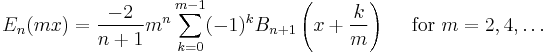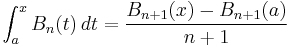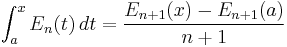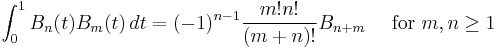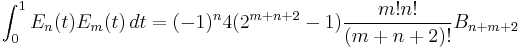Bernoulli polynomials
In mathematics, the Bernoulli polynomials occur in the study of many special functions and in particular the Riemann zeta function and the Hurwitz zeta function. This is in large part because they are an Appell sequence, i.e. a Sheffer sequence for the ordinary derivative operator. Unlike orthogonal polynomials, the Bernoulli polynomials are remarkable in that the number of crossings of the x-axis in the unit interval does not go up as the degree of the polynomials goes up. In the limit of large degree, the Bernoulli polynomials, appropriately scaled, approach the sine and cosine functions.
Representations
The Bernoulli polynomials Bn admit a variety of different representations. Which among them should be taken to be the definition may depend on one's purposes.
Explicit formula
for n ≥ 0, where bk are the Bernoulli numbers.
Generating functions
The generating function for the Bernoulli polynomials is
The generating function for the Euler polynomials is
Representation by a differential operator
The Bernoulli polynomials are also given by
where D = d/dx is differentiation with respect to x and the fraction is expanded as a formal power series.
Representation by an integral operator
The Bernoulli polynomials are the unique polynomials determined by
The integral operator
on polynomials f, is the same as
Another explicit formula
An explicit formula for the Bernoulli polynomials is given by
Note the remarkable similarity to the globally convergent series expression for the Hurwitz zeta function. Indeed, one has
where ζ(s, q) is the Hurwitz zeta; thus, in a certain sense, the Hurwitz zeta generalizes the Bernoulli polynomials to non-integer values of n.
The inner sum may be understood to be the nth forward difference of xm; that is,
where Δ is the forward difference operator. Thus, one may write
This formula may be derived from an identity appearing above as follows: since the forward difference operator Δ is equal to
where D is differentiation with respect to x, we have
As long as this operates on an mth-degree polynomial such as xm, one may let n go from 0 only up to m.
An integral representation for the Bernoulli polynomials is given by the Nörlund–Rice integral, which follows from the expression as a finite difference.
An explicit formula for the Euler polynomials is given by
This may also be written in terms of the Euler numbers Ek as
Sums of pth powers
We have
See Faulhaber's formula for more on this.
The Bernoulli and Euler numbers
The Bernoulli numbers are given by 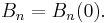 An alternate convention defines the Bernoulli numbers as
An alternate convention defines the Bernoulli numbers as 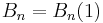 . This definition gives Bn = −nζ(1 − n) where for n = 0 and n = 1 the expression −nζ(1 − n) is to be understood as limx → n −xζ(1 − x). The two conventions differ only for n = 1 since B1(1) = 1/2 = −B1(0).
. This definition gives Bn = −nζ(1 − n) where for n = 0 and n = 1 the expression −nζ(1 − n) is to be understood as limx → n −xζ(1 − x). The two conventions differ only for n = 1 since B1(1) = 1/2 = −B1(0).
The Euler numbers are given by 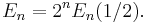
Explicit expressions for low degrees
The first few Bernoulli polynomials are:
The first few Euler polynomials are
Maximum and minimum
At higher n, the amount of variation in Bn(x) between x = 0 and x = 1 gets large. For instance,
which shows that the value at x = 0 (and at x = 1) is −3617/510 ≈ −7.09, while at x = 1/2, the value is 118518239/3342336 ≈ +7.09. D.H. Lehmer[1] showed that the maximum value of Bn(x) between 0 and 1 obeys
unless n is 2 modulo 4, in which case
(where 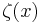 is the Riemann zeta function), while the minimum obeys
is the Riemann zeta function), while the minimum obeys
unless n is 0 modulo 4, in which case
These limits are quite close to the actual maximum and minimum, and Lehmer gives more accurate limits as well.
Differences and derivatives
The Bernoulli and Euler polynomials obey many relations from umbral calculus:
(Δ is the forward difference operator).
These polynomial sequences are Appell sequences:
Translations
These identities are also equivalent to saying that these polynomial sequences are Appell sequences. (Hermite polynomials are another example.)
Symmetries
Zhi-Wei Sun and Hao Pan [2] established the following surprising symmetric relation: If r + s + t = n and x + y + z = 1, then
where
Fourier series
The Fourier series of the Bernoulli polynomials is also a Dirichlet series, given by the expansion
This is a special case of the analogous form for the Hurwitz zeta function
This expansion is valid only for 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 when n ≥ 2 and is valid for 0 < x < 1 when n = 1.
The Fourier series of the Euler polynomials may also be calculated. Defining the functions
and
for 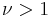 , the Euler polynomial has the Fourier series
, the Euler polynomial has the Fourier series
and
Note that the 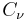 and
and 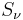 are odd and even, respectively:
are odd and even, respectively:
and
They are related to the Legendre chi function 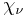 as
as
and
Inversion
The Bernoulli and Euler polynomials may be inverted to express the monomial in terms of the polynomials. Specifically, one has
and
Relation to falling factorial
The Bernoulli polynomials may be expanded in terms of the falling factorial 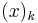 as
as
where 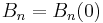 and
and
denotes the Stirling number of the second kind. The above may be inverted to express the falling factorial in terms of the Bernoulli polynomials:
where
denotes the Stirling number of the first kind.
Multiplication theorems
The multiplication theorems were given by Joseph Ludwig Raabe in 1851:
Integrals
Indefinite integrals
Definite integrals
Periodic Bernoulli polynomials
A periodic Bernoulli polynomial Pn(x) is a Bernoulli polynomial evaluated at the fractional part of the argument x. These functions are used to provide the remainder term in the Euler–Maclaurin formula relating sums to integrals. The first polynomial is a sawtooth function.
References
- ^ D.H. Lehmer, "On the Maxima and Minima of Bernoulli Polynomials", American Mathematical Monthly, volume 47, pages 533–538 (1940)
- ^ Zhi-Wei Sun; Hao Pan (2006). "Identities concerning Bernoulli and Euler polynomials". Acta Arithmetica 125: 21–39. arXiv:math/0409035.
- Milton Abramowitz and Irene A. Stegun, eds. Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables, (1972) Dover, New York. (See Chapter 23)
- Apostol, Tom M. (1976), Introduction to analytic number theory, Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics, New York-Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 978-0-387-90163-3, MR0434929 (See chapter 12.11)
- Dilcher, K. (2010), "Bernoulli and Euler Polynomials", in Olver, Frank W. J.; Lozier, Daniel M.; Boisvert, Ronald F. et al., NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0521192255, MR2723248, http://dlmf.nist.gov/24
- Cvijović, Djurdje; Klinowski, Jacek (1995). "New formulae for the Bernoulli and Euler polynomials at rational arguments". Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society 123: 1527–1535.
- Guillera, Jesus; Sondow, Jonathan (2008). "Double integrals and infinite products for some classical constants via analytic continuations of Lerch's transcendent". Ramanujan Journal 16 (3): 247–270. arXiv:math.NT/0506319. doi:10.1007/s11139-007-9102-0. (Reviews relationship to the Hurwitz zeta function and Lerch transcendent.)
- Hugh L. Montgomery; Robert C. Vaughan (2007). Multiplicative number theory I. Classical theory. Cambridge tracts in advanced mathematics. 97. Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press. pp. 495–519. ISBN 0-521-84903-9.
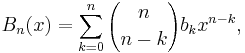
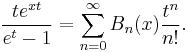
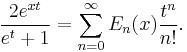
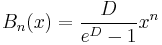
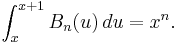
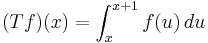
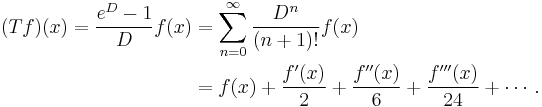
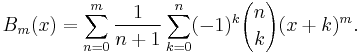
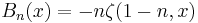
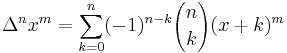
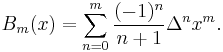
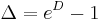
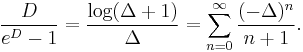
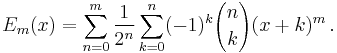
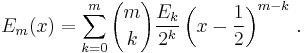
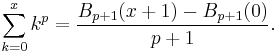
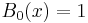
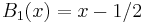
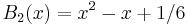
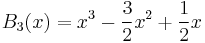
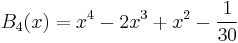
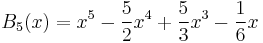
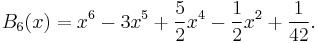
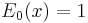
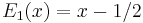
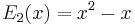
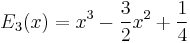
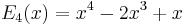
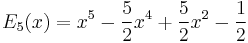
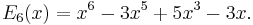
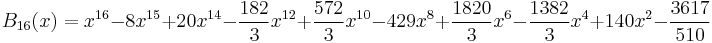
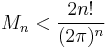
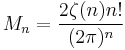
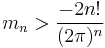
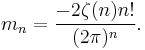
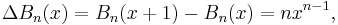
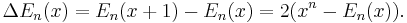
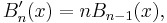
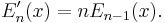
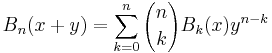
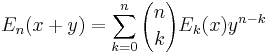
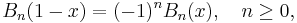
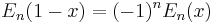
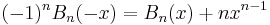
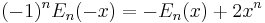
![r[s,t;x,y]_n%2Bs[t,r;y,z]_n%2Bt[r,s;z,x]_n=0,](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/ca1271a4485cff850535aa6153a45f9d.png)
![[s,t;x,y]_n=\sum_{k=0}^n(-1)^k{s \choose k}{t\choose {n-k}}
B_{n-k}(x)B_k(y).](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/4df16f477372fcad33f8d60371b612bd.png)
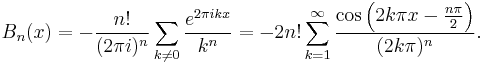
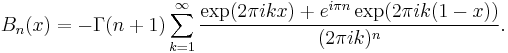
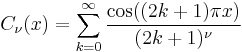
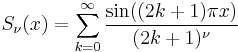
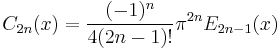
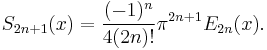
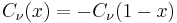
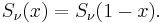
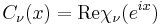
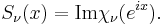
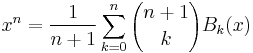
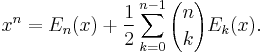
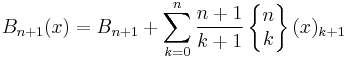
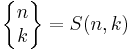
![(x)_{n%2B1} = \sum_{k=0}^n
\frac{n%2B1}{k%2B1}
\left[ \begin{matrix} n \\ k \end{matrix} \right]
\left(B_{k%2B1}(x) - B_{k%2B1} \right)](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/d61ba51dc90488ca411bc4adc31b248f.png)
![\left[ \begin{matrix} n \\ k \end{matrix} \right] = s(n,k)](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/283bfe964f7100bb222df00df8bd52b6.png)